What makes countries happier?
Research on what affects the levels of happiness of an individual, organization or country has been growing across different academic fields because of its importance to managers, business leaders and policy makers alike. The relationship between different measurements of income and happiness is multi-faceted. We presented this complexity in a chart recently. In this edition of the Criterion of the Month we explore how other important measures of The IMD World Competitiveness Ranking are related to the happiness of an economy.
Let’s begin by exploring the correlation between Happiness and Quality of Life. The vertical axis in Graph 1 presents the values from the 2018 UN World Happiness Report. The horizontal axis shows the IMD Executive Opinion Survey answers by mid- and upper- level business executives as to whether the quality of life is high in their country of residence. There is a strong positive relation with a correlation coefficient equal to 0.8 – the countries with high levels of subjective quality of life are also the countries that exhibit high levels of happiness.
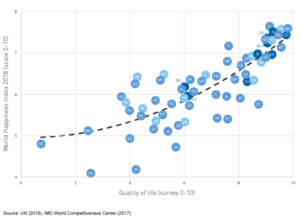
There are different grounds on which to formulate a subjective belief of a high quality of life. Undoubtedly, views about safety and justice as well as sentiments about environmental conditions and health provisions of a country are among the factors contributing to the quality of life. The IMD World Competitiveness Ranking uses a number of criteria that quantify these elements and aggregates them into various sub-factors.
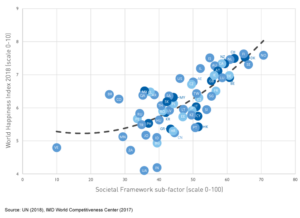
The Societal Framework sub-factor includes measures that capture components related to justice and security, private property rights, homicide, risk of political instability and social cohesion as well as measures of gender and income inequality in an economy. The higher the ranking in the Societal Framework, the lower the risk of negative effects in the above criteria. Graph 2 shows this association. Countries that fare strongly in issues related to personal safety and security as well as inclusiveness are associated with higher levels of happiness. The correlation coefficient is 0.7.
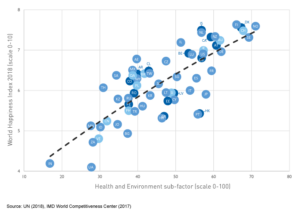
In addition to the current feelings about security and safety, one may have similar sentiments about living conditions. This is captured by the Health and Environment sub-factor, which captures both hard data and subjective opinions on issues related to the quality of the health infrastructure of a country as well as the environmental conditions related to ecological balance, pollution problems and environmental laws among others. Graph 3 portrays this positive relationship. Countries that exhibit high rankings in the Health and Environment sub-factor also demonstrate high levels of happiness. The correlation coefficient is 0.79.
Research related to the determinants of happiness as well as the impact of happiness on economic performance is growing. In this note, we show that using the IMD World Competitiveness Dataset, happiness is strongly related with high levels of safety and security, social inclusiveness, health infrastructure and environmental conditions. Policy makers should keep the above in mind when they work hard to improve the level of happiness of their citizens.
Research Information & Knowledge Hub for additional information on IMD publications
To understand America’s aggressive shift on trade, you must first grasp the silent, slow building, decades-long erosion of American middle-class prosperity. This shift began well before President Trump and will outlive him. It is rooted in the col...
Donald Trump has been called many things but his newest label – the great unifier of Europe – might just stick. That provocative notion may raise eyebrows in Brussels, Paris, or Berlin, but Mr Trump’s return could be the shock that finally compels...
Research Information & Knowledge Hub for additional information on IMD publications
Research Information & Knowledge Hub for additional information on IMD publications
Research Information & Knowledge Hub for additional information on IMD publications
Research Information & Knowledge Hub for additional information on IMD publications
in Gensler, Gary (Ed.); Johnson, Simon (Ed.); Panizza Ugo (Ed.); Weder di Mauro, Beatrice (Ed.) / The Economic Consequences of The Second Trump Administration: A Preliminary Assessment, pp. 239-244 / PAris: CEPR Press, 2025
Research Information & Knowledge Hub for additional information on IMD publications
Published by International Institute for Management Development ©2025
Research Information & Knowledge Hub for additional information on IMD publications
Research Information & Knowledge Hub for additional information on IMD publications
Research Information & Knowledge Hub for additional information on IMD publications
Research Information & Knowledge Hub for additional information on IMD publications
Research Information & Knowledge Hub for additional information on IMD publications









