IMD business school for management and leadership courses

Future Readiness Indicator
Automotive Future Readiness Indicator 2023
Beyond Tesla, who else in the auto industry is ready for the future? Experts at IMD can explain this in three graphs. Hint: BYD.
In today’s rapidly advancing world, future readiness has emerged as a pivotal benchmark, especially within the automotive industry. This term encapsulates an organization’s ability to anticipate, adapt to, and capitalize on emerging trends, technologies, and changes in consumer behavior.
As the global automotive landscape undergoes a transformative shift, marked by the advent of electric vehicles (EVs), increasing digital connectivity, and evolving environmental concerns, the ability to be future-ready distinguishes industry leaders from followers.
Within the comprehensive scope of IMD’s Future Readiness Indicator, the automotive industry stands as a significant category. IMD’s initiative spotlights various sectors, showcasing how each navigates the intricacies of innovation, sustainability, and market evolution.
Characteristics of a future-ready company
A future-ready company is one that not only adapts to change but thrives in it. This type of company is distinguished by several key characteristics:
- Agility. Companies that swiftly adapt to market changes and emerging technologies stay ahead of the curve. This includes the ability to pivot strategies, revise plans, and adopt new processes seamlessly.
- Innovation. Staying ahead often means continuous innovation. Future-ready companies invest in research and development, encourage creative thinking, and remain open to new ideas and methodologies.
- Technology adoption. A crucial aspect is the embrace of cutting-edge technology. Companies enhance efficiency and decision-making by leveraging digital tools, data analytics, and automation.
- Employee empowerment. Empowering employees with the skills and tools is necessary to succeed in a dynamic environment. This involves continuous learning opportunities, fostering a culture of collaboration, and offering flexible work arrangements.
- Customer centricity. Understanding customer needs and expectations deeply is a critical component. Future-ready companies personalize experiences, engage in meaningful interactions, and continually seek feedback for improvement.
- Sustainability. Reflecting a long-term vision, a commitment to sustainability involves implementing environmentally friendly practices, promoting social responsibility, and ensuring ethical governance.
- Global perspective. Having a global outlook helps in understanding diverse markets and cultures. This involves embracing diversity, understanding international trends, and being adaptable to global shifts.
- Resilience. Facing challenges with resilience is vital. Companies prepare for this with contingency plans, maintaining financial stability, and readiness for unforeseen circumstances.
Companies that embody these characteristics are better positioned to navigate the complexities of the modern business world and harness opportunities for growth and innovation.
Global automaker rankings
Below are the 2023 rankings for global automakers.
Click on the company’s name for key factors that make up the score. Drag the slider to adjust the year.
In what is arguably one of the most turbulent industries, carmakers have witnessed the meteoric rise of newer players like BYD and Xpeng as the industry pivots toward new capabilities such as chipset design, battery manufacturing, and software.
Tesla
Elon Musk’s Tesla continues to exemplify what it means to be at the forefront of future readiness in the automotive industry. Maintaining its top spot in the Automotive Future Readiness Indicator, Tesla’s success story is highlighted by its innovative approach to EVs and its strong commitment to sustainability.
Despite facing intense competition and market disruptions, Tesla has demonstrated remarkable resilience. This is reflected in its increased revenue and profit margins, proving its ability to adapt and thrive in a dynamic market environment.
Tesla’s quick adaptation to market dynamics and challenges, like the recall of 1.1 million cars in China, further underscores its innovative capabilities. Addressing potential safety issues through an over-the-air software update highlights Tesla’s agile response to problems and showcases its advanced approach to vehicle connectivity and customer service.
This incident is a testament to Tesla’s robust supply chain management and its prioritization of customer safety and satisfaction.
A pioneer in electrification, Tesla has played a pivotal role in the global shift toward EVs. The company’s advancements in this domain align with the increasing global focus on reducing emissions and promoting sustainability. Tesla’s impact is not limited to traditional automotive markets like the United States, Germany, and Japan but is also evident in emerging markets such as China and Singapore.
The company’s expansion strategies demonstrate a nuanced understanding of diverse market needs and consumer behaviors, contributing to its sustained dominance in the industry.
BYD
Warren Buffet-backed Chinese automaker BYD has made a remarkable ascent to the No. 2 spot in the Automotive Future Readiness Indicator, showcasing its significant role in the evolving automotive industry.
This impressive rise can largely be attributed to BYD’s substantial capabilities in producing both batteries and microchips, highlighting its commitment to self-sufficiency and innovation. As a key player in the EV market, BYD’s advancements reflect the growing global trend toward electrification and sustainable automotive solutions.
BYD’s approach to manufacturing, which integrates both battery production and microchip fabrication, sets it apart in an industry that’s increasingly reliant on these key components. This vertical integration ensures a stable supply chain—crucial in an era marked by frequent disruptions and shortages—and allows for greater control over the quality and innovation of its products.
BYD’s strategy of self-reliance is particularly noteworthy given the global challenges automakers face in securing essential components, further solidifying its position as a future-ready company.
Volkswagen
Volkswagen’s strategic emphasis on battery electric vehicles (BEVs) and autonomous vehicles has propelled it to secure the No. 3 position in the Automotive Future Readiness Indicator.
The company’s expansion in electric vehicles is a significant step toward reducing emissions and contributing to environmental sustainability. This move aligns VW with the global trend of electrification in the automotive industry, demonstrating its commitment to meeting current market demands and anticipating future trends.
Volkswagen’s ability to expand its global footprint through these initiatives indicates a robust and forward-thinking approach to business strategy. By investing in BEVs and autonomous vehicles, VW is diversifying its product offerings and enhancing its competitiveness in a market that increasingly values technological advancement and environmental responsibility.
Historical comparison of top carmakers
At IMD’s Center for Future Readiness, we gauge companies’ preparedness for the evolving future. Our quantitative approach utilizes hard market data, resulting in a balanced composite score.
The data feeding these rankings is sourced from company websites, annual reports, press releases, and news stories and is supplemented by third-party sources such as Crunchbase, Espacenet, and Google Trends. Read more about our methodology.
Compare historical trends by selecting top carmakers. Use the slider to adjust the years.
What is the future of the automotive industry?
As we can see, the industry is at a crossroads. Remember the semiconductor shortage or when you couldn’t get a new car even if you had the money to buy one? Thankfully, that time has passed. There are finally enough chipsets to go around, and production lines are running full-time again.
But, and it’s a very big but, it’s wrong to assume that things are back to normal. The reality is that chipset demand is likely to remain highly unpredictable. Such demand is affected by the speed of the rollout of new technologies like AI, cloud computing, the Internet of Things (IoT), and 5G or 6G.
On the supply side, chipset factories typically run close to maximum capacity. That leaves the production system extremely susceptible to disruptions. Natural disasters like earthquakes and floods can cause major problems, as can accidents such as fires and power outages. Geopolitical or military tensions, including those between the U.S. and China, could also pose challenges.
That’s why top-ranking carmakers are aggressively cultivating in-house expertise in microchip sets. Rather than relying on suppliers or subsuppliers for semiconductors, they are directly engaging with chipmakers and doing the relevant designs in-house. For instance, Ford collaborated with U.S. chipmaker GlobalFoundries to create chips for its vehicles while exploring the prospect of expanding its domestic chip production. Such an approach has already been commonplace among the newer players. Tesla, BYD, and Xpeng all have extensive operations dedicated to designing or even producing their own chipsets.
What this implies is a fundamental shift in the core capabilities of carmakers. Historically, VW, GM, and Toyota all focused on final assembly. From the boardroom to the shop floor, their expertise lay with mechanical engineers.
Now, expertise is becoming digital, emphasizing software. This requires a faster decision-making pace and the ability to avoid being inhibited by hierarchy and bureaucracy.
You may wonder: Is this shift toward faster decision-making and less bureaucracy really happening?
Digital orientation vs. decision speed
For our final analysis, we built an AI algorithm that sifted through 70 news sources—including The Financial Times, The Wall Street Journal, annual reports, and earning announcements—analyzing over 10 years’ worth of reports.
We then fed this information into the system to conduct a sentiment analysis in a big-data style. Read more about how we did this.
The following visual shows the overall behavior of different companies.
A picture is worth a thousand words, and the graph demonstrates that traditional carmakers need to move faster and become digital-first. The world has no time to wait.
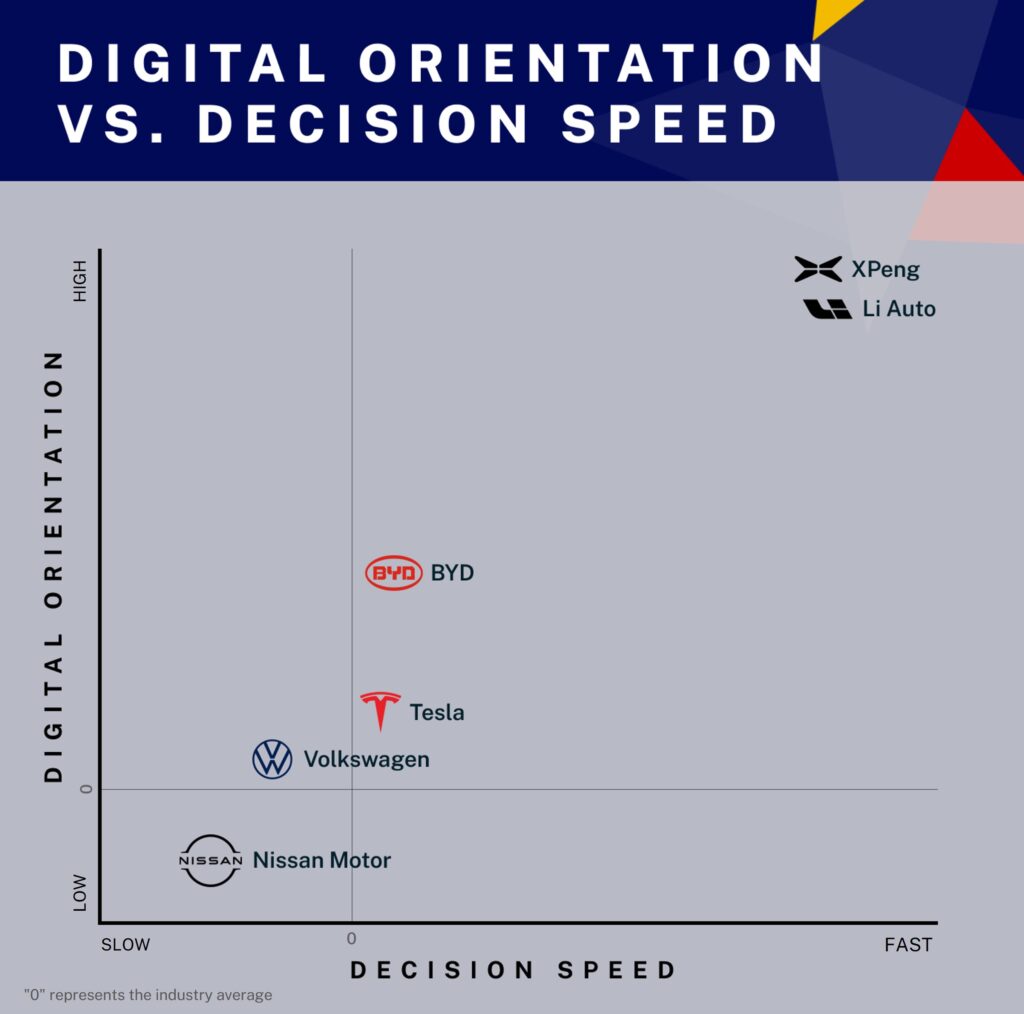
That’s why we conduct a final analysis. We’ve built an AI algorithm that has sifted through 70 news sources, analyzing over 10 years’ worth of reports. The Financial Times, Wall Street Journal, annual reports, earning announcements—we feed all this information into the system to conduct a sort of sentiment analysis in a big-data style. Again, you can read more about how we do this here. The result is the picture you see above, which shows the overall behavior of different companies.
A picture is worth a thousand words, and the above picture demonstrates that traditional carmakers need an overhaul of their disposition. They need to move faster and become digital-first. The world has no time to wait.